What Are Helium Release Valves?

In the realm of haute horlogerie, where precision meets innovation, few components are as intriguing and specialized as the helium release valve (HRV). Often misunderstood and sometimes controversial, these tiny mechanisms play a crucial role in the world of professional diving watches. But what exactly are helium release valves, and why do they matter? Let's embark on a journey to the depths of watchmaking engineering and underwater exploration to uncover the secrets of these fascinating devices.
The Science Behind Helium Release Valves
To understand the purpose of helium release valves, we must first delve into the unique properties of helium and the extreme conditions encountered in deep-sea diving.
Helium: The Sneaky Noble Gas
Helium is the second lightest and second most abundant element in the observable universe. As a noble gas, it's chemically inert, which makes it ideal for use in diving. However, its small atomic size gives it a remarkable ability to penetrate materials that are impermeable to other gases.
This chart illustrates why helium poses a unique challenge in diving watches. Its small size allows it to seep into watch cases where other gases cannot.
This chart illustrates why helium poses a unique challenge in diving watches. Its small size allows it to seep into watch cases where other gases cannot.
Saturation Diving: Pushing the Limits
Saturation diving is a technique used for extended deep-sea operations. Divers live in pressurized environments for days or weeks, breathing a mixture of oxygen and helium known as heliox. This method allows for longer bottom times and reduced decompression periods.
During these dives, the ambient pressure can reach extremes that would crush conventional equipment. For context:
| Depth (meters) | Pressure (atmospheres) |
|---|---|
| Surface | 1 |
| 10 | 2 |
| 100 | 11 |
| 300 | 31 |
| 500 | 51 |
At these pressures, helium atoms can slowly penetrate the seals of a dive watch, accumulating inside the case.
The Helium Problem in Dive Watches
As divers return to the surface and undergo decompression, the external pressure decreases. However, the helium trapped inside the watch cannot escape as quickly, creating a pressure differential. This internal pressure can cause damage to the watch, from popping off the crystal to damaging internal components.
This is where the helium release valve comes into play.
How Helium Release Valves Work
Helium release valves are ingenious solutions to a very specific problem. They come in two main types: manual and automatic.
Manual Helium Release Valves
Manual HRVs are typically small, screw-down crowns positioned on the side of the watch case. During decompression, the diver manually unscrews the valve, allowing the trapped helium to escape and equalizing the pressure.
Automatic Helium Release Valves
Automatic HRVs are more sophisticated. They contain a small, spring-loaded valve that activates when the internal pressure exceeds a certain threshold, typically around 3 to 5 atmospheres of pressure differential.
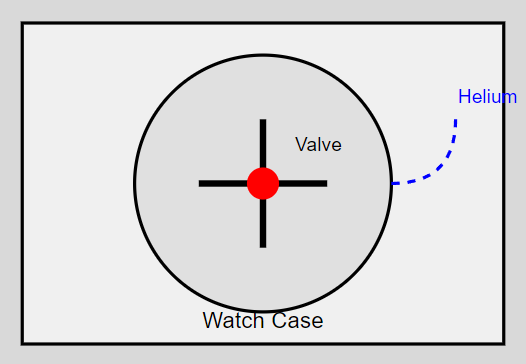
This diagram illustrates the basic principle of an automatic helium release valve. When the internal pressure (represented by the blue dashed line) exceeds a certain threshold, the valve (red circle) opens, allowing the helium to escape.
Helium Release Valves in Professional Diving
While HRVs may seem like a niche feature, they are critical for commercial divers and underwater construction workers who spend extended periods at great depths.
Applications in Commercial Diving
Commercial diving operations often involve tasks such as:
- Offshore oil and gas platform maintenance
- Underwater welding and construction
- Scientific research in deep-sea environments
- Salvage operations
In these scenarios, divers may spend weeks living in pressurized habitats, making the HRV an essential feature of their equipment.
The Decompression Process
The decompression process is where HRVs truly prove their worth. As divers ascend, they must make stops at various depths to allow dissolved gases to safely exit their tissues. This process can take days for extreme dives.
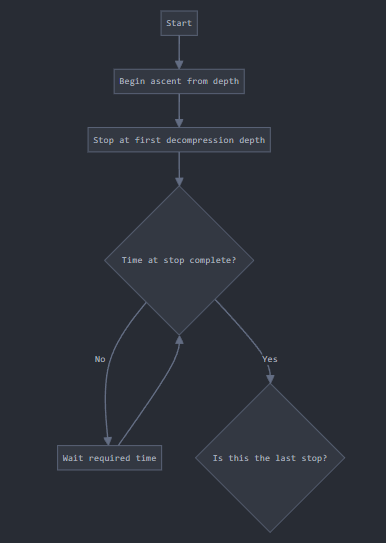
This simplified decompression chart shows the staged ascent process. During each stop, the HRV allows accumulated helium to escape from the watch, preventing damage.
Iconic Dive Watches with Helium Release Valves
Several luxury watch brands have made their mark with innovative HRV designs.
Rolex Sea-Dweller
Rolex pioneered the HRV with the Sea-Dweller, introduced in 1967. The Sea-Dweller was developed in collaboration with COMEX, a professional diving company, to meet the needs of saturation divers.
Key features of the Rolex HRV:
- Patented Gas Escape Valve
- Automatically releases helium and other gases
- Integral part of the Oyster case design
Omega Seamaster Diver 300M
Omega's approach to the HRV is distinctive, with a manual release valve prominently placed at the 10 o'clock position.
Notable aspects:
- Manual operation allows for testing and maintenance
- Distinctive aesthetic element
- Featured in James Bond films, adding to its pop culture status
Comparative Analysis
Let's compare some popular dive watches with HRVs:
| Brand | Model | HRV Type | Depth Rating | Price Range (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rolex | Sea-Dweller | Automatic | 1,220m | 11,700 - 16,600 |
| Omega | Seamaster Diver 300M | Manual | 300m | 5,200 - 9,700 |
| Doxa | Sub 300T | Automatic | 1,200m | 1,890 - 2,490 |
| Tudor | Pelagos | Automatic | 500m | 4,575 - 4,925 |
Controversies and Debates
Despite their crucial role in professional diving, HRVs are not without controversy in the watch community.
Necessity for Recreational Divers
Many argue that HRVs are unnecessary for recreational divers who rarely, if ever, engage in saturation diving. Critics point out that for most dive watch wearers, an HRV is more of a marketing feature than a practical tool.
Impact on Water Resistance
There's ongoing debate about whether HRVs, especially manual ones, can compromise a watch's water resistance if not properly maintained or operated.
Aesthetic Considerations
The presence of an HRV, particularly manual valves, can significantly alter a watch's appearance. While some appreciate the technical look, others find it disrupts the clean lines of a classic dive watch design.
Future of Helium Release Valves
As with all technology, HRVs continue to evolve. Several trends are shaping their future:
Advancements in Valve Technology
Manufacturers are constantly refining HRV designs to improve reliability and reduce size. Some recent innovations include:
- Micro-machined valves for greater precision
- New materials that are more resistant to helium penetration
- Integration of HRVs with other functions, such as pressure sensors
Alternative Solutions
Some watchmakers are exploring alternatives to traditional HRVs:
- Advanced case materials that are naturally more resistant to helium ingress
- Flexible case designs that can withstand internal pressure without a dedicated valve
- Digital dive computers with integrated pressure sensors that eliminate the need for mechanical solutions
Changing Trends in Professional Diving
As diving technology evolves, so too do the needs of professional divers:
- Increased use of remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) for some tasks previously done by saturation divers
- Development of new breathing gas mixtures that may alter decompression protocols
- Advancements in decompression algorithms that could change dive profiles
These changes may influence the future relevance and design of HRVs in professional dive watches.
Conclusion
Helium release valves represent a fascinating intersection of horology and marine engineering. Born out of necessity for the most extreme diving conditions, they have become a hallmark of professional-grade dive watches.
While their practical application may be limited for most watch wearers, HRVs continue to captivate enthusiasts as a symbol of human ingenuity and our enduring fascination with exploring the depths. They stand as a testament to the watch industry's commitment to pushing the boundaries of what's possible in mechanical timepieces.
As we look to the future, the evolution of HRVs will likely be driven by advancements in materials science, changing diving practices, and the ever-present desire for innovation in luxury watchmaking. Whether they remain a crucial tool for professional divers or become a nostalgic nod to the golden age of underwater exploration, helium release valves have undoubtedly earned their place in the annals of horological history.
In the end, these tiny valves tell a much bigger story – one of human ambition, engineering prowess, and the relentless pursuit of conquering new frontiers, both above and below the waves.